Untangling Prefix Delegations by Internet Registries
Understanding the delegation status values in WHOIS data from RIRs
Introduction
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is responsible for global IP address allocation among the five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs). The five RIRs manage the resources they have been allocated by IANA and further assign resources to customer organizations. The customer organizations can be National Internet Registries (NIRs), Local Internet Registries (LIRs), Internet Service Providers (ISPs) or end-user organizations.
The five RIRs operate in different regions of the world and autonomously decide the delegation hierarchy and usage terms of the IP address blocks they delegate. These terms of usage can be inferred from the WHOIS database, which records registration information of Internet Resources and is considered to be the authoritative source of information since this dataset is managed by network operators and resource holders. In the WHOIS dataset, RIRs use the status or NetType attribute to indicate the delegation status. RIRs use different values for these fields and in this blog, we decode the keywords used and the delegation hierarchy of each RIR.
Note : In this post we indicate LIRs as ISPs for the sake of brevity. LIRs are generally ISPs but all ISPs are not LIRs. LIRs get address blocks directly from the RIRs and can further delegate the address blocks to their customers like ISPs. ISPs are organizations that provide Internet services to customers and can get address blocks from LIRs or other ISPs.
Data
In this study we use the bulk WHOIS data from five RIRs. WHOIS data contains information about IP address blocks, their delegation status, the organization who has been delegated the address space, Autonomous System Numbers, domain names, and even contact details of network administrators. This data is publicly available and can be accessed through the WHOIS protocol
WHOIS data consists of several types of records such as inetnum, inet6num, aut-num, domain, organisation, person, route and route6. Each record serves a different purpose. For instance, the inetnum record contains information about an IPv4 address block, the aut-num record contains information about an Autonomous System Number(ASN), and the organisation record contains information about an organization registered with an RIR. In this study, we investigate the inetnum and inet6num records to infer the delegation status of the IPv4 and IPv6 address blocks respectively. Note that route and route6 records also contain information about IPv4 and IPv6 prefixes, but this object serves to record the routing policies of an organization and hence, it is not used in this study.
Delegation Status Attributes and Values
Different RIRs use different keywords to indicate the delegation status of an IP address block. In this section, we decode the keywords used by each RIR and the delegation hierarchy. The delegation hierarchy is not explicitly mentioned in the WHOIS data, but we infer the hierarchy based on the keywords used by the RIRs. The hierarchy is represented as a directed acyclic graph where the root node represents the IANA and the leaf nodes represent the end-user organizations. The edges represent the delegation of an IP address block from one organization to another. The hierarchy is inferred based on the delegation status of the IP address blocks and the organization that has been delegated the address block.
Note that all RIRs do not provide a documentation of the keywords they use to indicate the delegation status of an IP address block. The keywords and the indicated delegation status used by each RIR are listed below. Check the Appendix for a sample WHOIS data from each RIR.
ARIN
ARIN uses the NetType key to indicate the delegation status of an IP address block. The NetType key can have the values - ALLOCATION, ASSIGNMENT, REALLOCATION, REASSIGNMENT, RIR and RESERVED. The values indicate the following:
- ALLOCATION : IP address block has been directly allocated by ARIN to an LIR or ISP. Since it is a direct allocation by ARIN, the address block is portable i.e. if the organization changes its upstream provider, it can retain the address block
. - REALLOCATION : IP address block has been reallocated by the LIR or ISP to a downstream customer. The address block is not portable and the downstream entity must return the address space when changing providers.
- ASSIGNMENT : IP address block has been reserved by IANA for special purposes
These address blocks are more commonly known as bogon prefixes. The complete list can be found here. . - REASSIGNMENT : IP address block has been reassigned to an end-user organization and cannot be further delegated. The organization must use the address block within its own infrastructure. The address block is not portable and the end-user must return the address space when changing providers.
- RIR : IP address block has been delegated to either self or other RIRs by ARIN.
- RESERVED : IP address block has been reserved by IANA.
ARIN consists of a simple hierarchy where the IP address blocks are directly allocated by ARIN to ISPs. The ISPs can further reallocate the address blocks to downstream customers or reassign them to end users. The end users cannot further delegate the address blocks. ARIN consists of $3.1M$ IPv4 ($300K$ IPv6) records and $96.0$% ($93.3$%) of these records are assignments to the end users. Note that ISPs often have one WHOIS record for a large address block and they create several records for the smaller address blocks they delegte to their customers. Table 1 summarizes the distribution of the delegation status of ARIN WHOIS records.
| ARIN | inetnum | inet6num |
|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATION | 2.3% | 3.23% |
| ASSIGNMENT | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| REASSIGNMENT | 96.04% | 93.28% |
| RIR | 0.24% | 0.01% |
| REALLOCATION | 1.43% | 3.47% |
| RESERVED | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Total records | 3,158,560 | 299,535 |
Table 1 : Distribution of IP address delegation types for IPv4 (inetnum) and IPv6 (inet6num) records in ARIN
LACNIC
LACNIC indicates the delegation type in the status key of its WHOIS data. The status key can have the values - ALLOCATED, REALLOCATED, ASSIGNED and REASSIGNED. Similar to the keywords used by ARIN, the status values indicate the following:
- ALLOCATED : IP address block has been directly allocated by LACNIC to an LIR or ISP.
- REALLOCATED : IP address block has been reallocated by the LIR or ISP to a downstream customer.
- ASSIGNED : IP address block has been assigned directly by the RIR to an organization and can be reassigned to an end-user organization.
- REASSIGNED : IP address block has been reassigned to an end-user organization and cannot be further delegated. The organization must use the address block within its own infrastructure.
The LACNIC hierarchy is similar to the ARIN hierarchy. The IP address blocks are directly allocated by LACNIC to ISPs. The ISPs can further reallocate the address blocks to downstream customers or reassign them to end users. LACNIC consists of $466K$ IPv4 and $28K$ IPv6 records. $71.86$% of the IPv4 records are reallocations by the ISPs. in contrast, the IPv6 delegations are have a bimodal distribution where $40.0$% records are allocations and $41.0$% records are reallocations. Due to the generous availability of IPv6 addresses, LACNIC performs numerous direct allocations to organizations. The following table summarizes the distribution of the delegation status of LACNIC WHOIS records. Refer to Table 2 for the distribution of delegation types in LACNIC.
| LACNIC | inetnum | inet6num |
|---|---|---|
| ASSIGNED | 0.55% | 5.57% |
| ALLOCATED | 3.61% | 40.0% |
| REALLOCATED | 71.86% | 41.01% |
| REASSIGNED | 23.99% | 13.42% |
| Total records | 466,256 | 28,022 |
Table 2 : Distribution of IP address delegation types for IPv4 (inetnum) and IPv6 (inet6num) records in LACNIC
AFRINIC and RIPE
AFRINIC and RIPE use the same set of values to indicate the delegation status of an IP address block. They use the status field to indicate the delegation status of an IP address block. The status field can have values such as ALLOCATED PA, ASSIGNED PI, ASSIGNED PA and SUB-ALLOCATED PA. We first define some of the common terminologies used by AFRINIC and RIPE.
Terminologies
-
Provider Aggregatable (PA) : These address blocks are allocated to ISPs and are designed to be aggregated while making route announcements on BGP. ISPs can sub-allocate or assign smaller blocks to their customers and are responsible for maintaining the registration information with the RIRs. These address blocks are considered non-portable since the customers have to relinquish the address block when changing providers
. -
Provider Independent (PI) : These address blocks are assigned to an end-user organization directly by an RIR and allow the holder to retain the allocation independent of their upstream provider (thus, considered portable). While these allocations offer more flexibility to the end-user, it increases the load on the global routing table since the address blocks have to be announced individually on BGP and cannot be aggregated with other PA address blocks. These address blocks are increasingly rare in IPv4 due to the depletion of IPv4 addresses and the increased pressure for routing aggregation. RIPE has stopped issuing PI IPv4 address blocks but can still issue PI IPv6 address blocks.
-
Sub-allocation - Sub-allocations allow an ISP to distribute smaller blocks of its non-portable address space to downstream entities who can make further assignments to end-users. ISPs holding ALLOCATED UNSPECIFIED allocations may be able to convert them to PA allocations if there are no ASSIGNED PI networks within it (more on these status values in next subsection). The ISPs are responsible for maintaining the registration information with the RIRs. They are also recommended to ensure that the downstream customers return the assigned address space when chaging their service providers
.
Description
The most common values used by AFRNIC and RIPE indicate the following
- ALLOCATED PA : IP address block has been directly allocated by the RIR to an ISP. It can be further sub-allocated or assigned to downstream customers, but the downstream entity must return the address space when changing providers.
- ASSIGNED PI : IP address block has been assigned by the RIR to an end-user organization. The end-user can change upstream providers without returning the address space.
- SUB-ALLOCATED PA : IP address block has been sub-allocated by an ISP to a downstream customer. The downstream customer can further assign address blocks to its own customers. The address block must be returned to the ISP when changing providers.
- ASSIGNED PA : IP address block has been assigned by an network provider to an end-user organization and cannot be further delegated.
- LEGACY : IP address block was assigned to an organization prior to the formation of the RIRs. These address blocks are not subject to the same policies as the other address blocks and are not managed by the RIRs.
- LIR-PARTITIONED PA : LIRs manage this block within their organization. This address block is considered not used and more specific address blocks should be registered.
Some of the values found only in inet6num i.e. IPv6 address blocks are
- ALLOCATED-BY-RIR : IP address block has been directly allocated by the RIR to an ISP.
- ALLOCATED-BY-LIR : This status value is equivalent to the SUB-ALLOCATED PA attribute. IP address block has been allocated by an LIR to sub-ordinate ISPs.
- AGGREGATED-BY-LIR : IP address block has been aggregated by an LIR from smaller assignments to multiple customers. The smaller assignments must be of the same size and the size is mentioned in the
assignment-sizeattribute of the record. - ASSIGNED : IP address block has been assigned by an LIR to self or an end-user organization.
Table 3 offers a concise description of the most common delegation status values and their characteristics in AFRINIC and RIPE.
| Status | Allocation made by | Allocation made to | Allocation can be retained? | Further delegation permitted? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED PA | RIR | LIR | - | Yes |
| SUB-ALLOCATED PA | LIR | Network Operators | No | Yes |
| ASSIGNED PA | LIR | End user/Self | No | No |
| ASSIGNED PI | RIR | End user | Yes | No |
Table 3 : Delegation types and usage terms in AFRINIC and RIPE
Fig 1 and Fig 2 show the delegation hierarchy of IPv4 and IPv6 records respectively. AFRINIC consists of $154K$ IPv4 and $32K$ IPv6 records while RIPE consists of $4.3M$ IPv4 and $884K$ IPv6 records. Similar to ARIN, $96.4$% IPv4, $95.7$% IPv6 records in AFRINIC and $94.2$% IPv4, $87.6$% IPv6 RIPE records are non-portable assignments to end users. Refer to Table 4 and Table 5 for the distribution of delegation types in AFRINIC and RIPE.
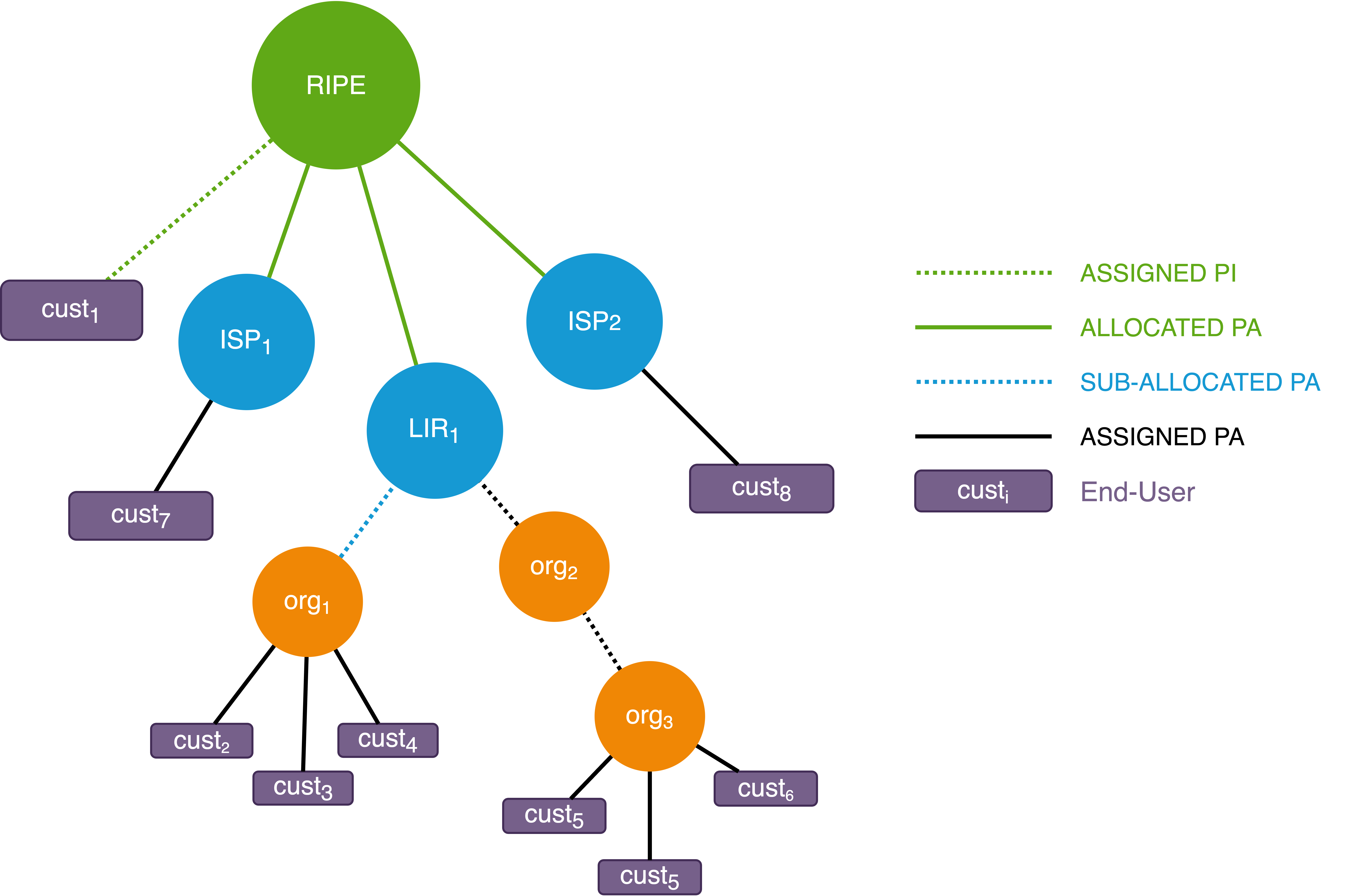
AFRINIC and RIPE IPv4 delegation hierarchy (simplified)
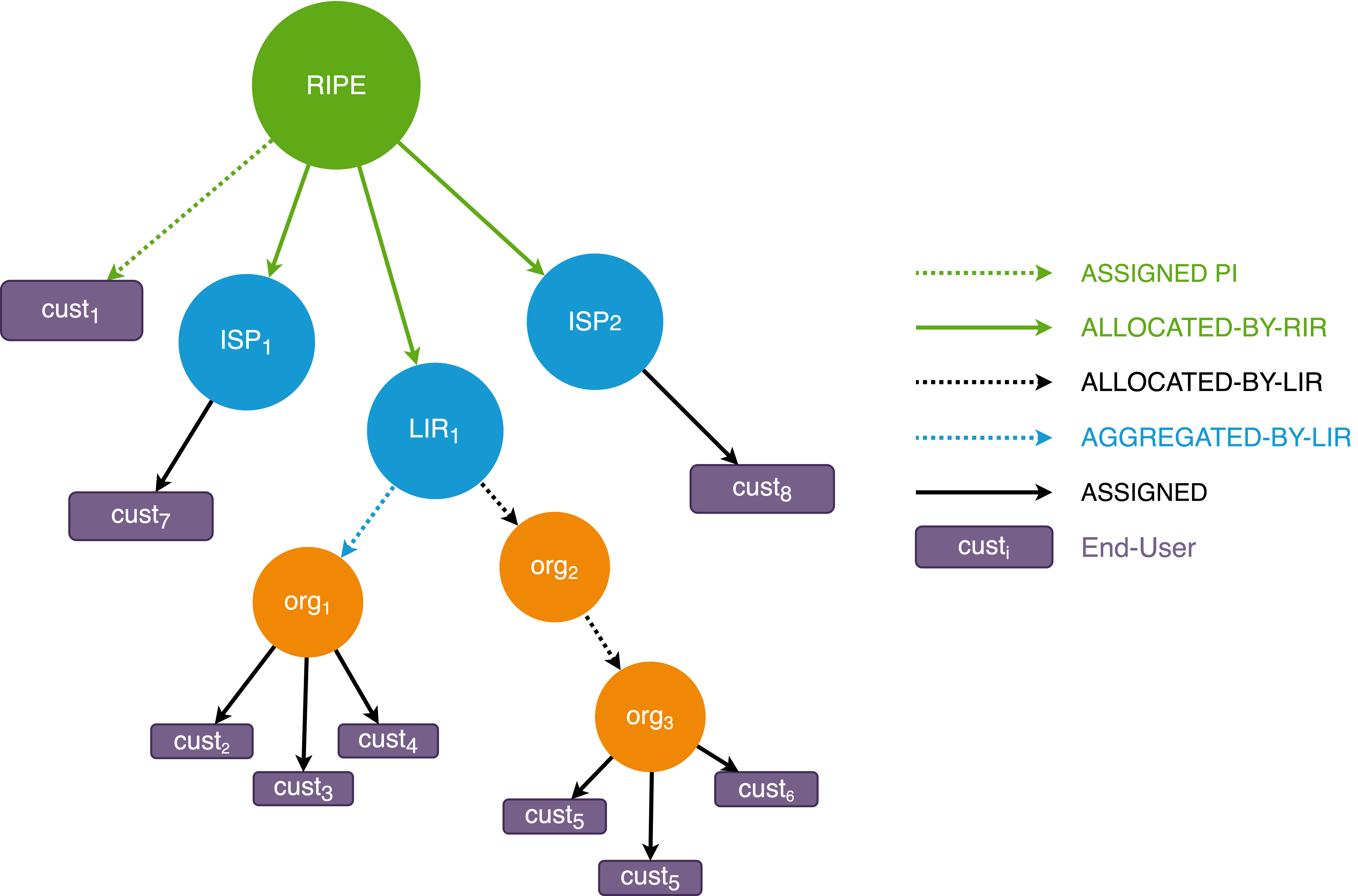
RIPE IPv6 delegation hierarchy (simplified)
| AFRINIC | inetnum | inet6num |
|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED PA | 2.19% | - |
| SUB-ALLOCATED PA | 0.23% | - |
| ASSIGNED PA | 96.41% | 95.67% |
| ASSIGNED PI | 1.06% | 1.02% |
| ALLOCATED UNSPECIFIED | 0.1% | 0.01% |
| ASSIGNED ANYCAST | 0.01% | 0.01% |
| POLICY-RESERVED | 0.0% | - |
| ALLOCATED-BY-RIR | - | 3.29% |
| Total records | 153,711 | 32,162 |
Table 4 : Distribution of IP address delegation types for IPv4 (inetnum) and IPv6 (inet6num) records in AFRINIC
| RIPE | inetnum | inet6num |
|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED PA | 1.55% | - |
| SUB-ALLOCATED PA | 0.27% | - |
| ASSIGNED PA | 94.21% | - |
| ALLOCATED-ASSIGNED PA | 0.0% | - |
| ASSIGNED PI | 0.47% | 0.43% |
| ASSIGNED ANYCAST | 0.0% | 0.01% |
| ASSIGNED | - | 87.64% |
| ALLOCATED-BY-RIR | - | 2.56% |
| ALLOCATED-BY-LIR | - | 2.07% |
| AGGREGATED-BY-LIR | - | 7.29% |
| LIR-PARTITIONED PA | 0.31% | - |
| ALLOCATED UNSPECIFIED | 0.3% | - |
| LEGACY | 2.9% | - |
| Total records | 4,325,375 | 884,387 |
Table 5 : Distribution of IP address delegation types for IPv4 (inetnum) and IPv6 (inet6num) records in RIPE
APNIC
APNIC uses the status field to indicate the delegation status of an IP address block. The status field can have the values - ALLOCATED PORTABLE, ALLOCATED NON-PORTABLE, ASSIGNED PORTABLE and ASSIGNED NON-PORTABLE. The values indicate the following
- ALLOCATED PORTABLE : IP address block has been directly allocated by APNIC to an ISP and can be further sub-allocated or assigned to downstream customers.
- ALLOCATED NON-PORTABLE : IP address block has been directly allocated by an ISP to their customers. The address block has to be returned to the provider when changing the upstream provider.
- ASSIGNED PORTABLE : IP address block has been assigned by APNIC to small-multihoming organizations or IXPs. These assignments can be retained by the customer while changing the network provider.
- ASSIGNED NON-PORTABLE : IP address block has been assigned by an ISP to an end-user organization and cannot be further delegated. The address block has to be returned to the provider when changing the upstream provider.
APNIC consists of $1.26M$ IPv4 and $104K$ IPv6 records. $88.1$% IPv4 and $73.7$% IPv6 records are non-portable assignments to end users. Refer to Table 6 for the distribution of delegation types in APNIC.
| APNIC | inetnum | inet6num |
|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED PORTABLE | 3.31% | 8.52% |
| ALLOCATED NON-PORTABLE | 7.52% | 11.9% |
| ASSIGNED PORTABLE | 1.06% | 5.9% |
| ASSIGNED NON-PORTABLE | 88.1% | 73.68% |
| Total records | 1,263,350 | 104,028 |
Table 6 : Distribution of IP address delegation types for IPv4 (inetnum) and IPv6 (inet6num) records in APNIC
Applications
The delegation status of an IP address block reveals several critical information about an address block. We can build the complete delegation tree of an address block to understand how the address block is being used on the Internet. The portability status of an address block can inform us if the address block has been potentially used by multiple organizations. We can also determine if routes to the block can be aggregated with other addresses, which can help us optimize the size of routing tables on BGP. This data can also aid us in understanding the fragmentation of address blocks which again directly impacts BGP routing table size, resource certificates in the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). The delegation hierarchy also reveals business operations of organizations i.e. which organizations are ISPs, which organizations sub-allocate address spaces to others, and which organizations are end-users. This information can be used to understand the business relationships between organizations and the structure of the Internet.
Who can issue RPKI certificates?
In this section we use the delegation status to understand which organizations issue RPKI certificates for an IP address block. RPKI certificates or Route Origin Authorizations (ROAs) are used to validate the origin of a route announcement on BGP. The RPKI certificates can be issued by the entity which has authoritative control over the Internet resource. Due to the complex and distinct delegation hierarchy across the RIRs, finding the entity which can issue RPKI certificates for an IP address block can be challenging.
If an IP address block was directly allocated to Org A and it further sub-allocates a part of the block to Org B, who can issue RPKI certificates for the smaller address block - Org A or Org B? We can answer to this question by studying the delegation status of the address blocks. Table 7 summarizes the delegation status of an IP address block and the organization that can issue ROAs for the address block.
Methodology
We extract resource certificates from the RPKI repository and match the IP address blocks in the certificates with the WHOIS data. We then infer the delegation status of the address block and the organization that can issue ROAs for the address block. We summarize the results in Table 7.
We source the RPKI data from the certificate archive created using the RPKI Client tool. The RPKI console can also be used to navigate the certificate archive on a web browser.
Results
| RIR | IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|---|
| ARIN | ALLOCATED | ALLOCATED |
| LACNIC | ALLOCATED, ASSIGNED | ALLOCATED, ASSIGNED |
| RIPE | ALLOCATED PA, ASSIGNED PI, LEGACY | ALLOCATED-BY-RIR, ASSIGNED PI |
| AFRINIC | ALLOCATED PA, ASSIGNED PI | ALLOCATED-BY-RIR, ASSIGNED PI |
| APNIC | ALLOCATED PORTABLE, ASSIGNED PORTABLE | ALLOCATED PORTABLE, ASSIGNED PORTABLE |
Table 7 : Which delegation status indicates the organization has the authority to issue ROAs for the address block?
Note : In RIPE, sub-delegations from a LEGACY address block are also considered LEGACY. But the organization holding the parent address block can issue ROAs for the sub-delegated address block.
Conclusion
In this blog we decoded the delegation status values used by the RIRs in the WHOIS data. We inferred the delegation hierarchy of the RIRs and understood the delegation status of the IP address blocks. The delegation status values can be used to understand the hierarchy of the Internet resources and the business relationships between organizations. The delegation status values can also be used to understand the portability of an address block and the aggregation of routes on BGP. We also used the delegation status values to understand which organizations can issue RPKI certificates for an IP address block.
If you found this useful, please cite this as:
Gouda, Deepak (Aug 2024). Untangling Prefix Delegations by Internet Registries. https://deepakgouda.github.io.
or as a BibTeX entry:
@article{deepak2024untangling-prefix-delegations,
title = {Untangling Prefix Delegations by Internet Registries},
author = {Gouda, Deepak},
year = {2024},
month = {Aug},
url = {https://deepakgouda.github.io/blog/2024/whois/}
}
Appendix
WHOIS Data Samples
ARIN WHOIS data sample
NetHandle: NET-220-158-32-0-1
OrgID: ORACLE-4
Parent: NET-220-0-0-0-1
NetName: ORACLE-4
NetRange: 220.158.32.0 - 220.158.47.255
NetType: allocation
RegDate: 2024-06-26
Updated: 2024-06-26
Source: ARIN
LACNIC WHOIS data sample
inetnum: 24.152.4/22
status: allocated
owner: JNET TELECOM
city: Manaus
country: BR
owner-c: JLB42
tech-c: JLB42
abuse-c: JLB42
inetrev: 24.152.4/22
nserver: NS1.JNETTELECOM-AM.COM.BR
nserver: NS2.JNETTELECOM-AM.COM.BR
created: 2020-03-12
changed: 2020-03-12
source: LACNIC
AFRINIC WHOIS data sample
inetnum: 196.202.192.0 - 196.202.223.255
netname: KE-KPTC-20041025
descr: PROVIDER Local Registry
descr: Kenyan Post & Telecommunications
country: KE
admin-c: LO8-AFRINIC
tech-c: MKN1-AFRINIC
tech-c: GKN1-AFRINIC
org: ORG-KPTC1-AFRINIC
status: ALLOCATED PA
mnt-by: AFRINIC-HM-MNT
mnt-lower: KPTC-MNT
mnt-domains: KPTC-MNT
remarks: data has been transferred from RIPE Whois Database 20050221
notify: ***@orange-tkl.co.ke
notify: ***@orange-tkl.co.ke
notify: ***@orange-tkl.co.ke
changed: ***@ripe.net 20041025
changed: ***@afrinic.net 20050205
changed: ***@afrinic.net 20121214
source: AFRINIC
APNIC WHOIS data sample
inetnum: 202.6.91.0 - 202.6.91.255
netname: NLA-AU
descr: National Library of Australia
country: AU
org: ORG-NLOA1-AP
admin-c: NC68-AP
tech-c: NC68-AP
abuse-c: AN649-AP
status: ASSIGNED PORTABLE
remarks: --------------------------------------------------------
remarks: To report network abuse, please contact mnt-irt
remarks: For troubleshooting, please contact tech-c and admin-c
remarks: Report invalid contact via www.apnic.net/invalidcontact
remarks: --------------------------------------------------------
mnt-by: APNIC-HM
mnt-routes: MAINT-AU-NLA
mnt-irt: IRT-NLA-NON-AU
last-modified: 2023-02-17T08:17:38Z
source: APNIC
RIPE WHOIS data sample
inetnum: 217.204.204.224 - 217.204.204.231
netname: WESLEYLOWE
descr: Wesley Lowe
descr: Office
descr: Bolton, Lancs.
country: GB
admin-c: DUMY-RIPE
tech-c: DUMY-RIPE
status: ASSIGNED PA
mnt-by: EASYNET-UK-MNT
created: 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z
last-modified: 2001-09-21T22:08:06Z
source: RIPE
remarks: ****************************
remarks: * THIS OBJECT IS MODIFIED
remarks: * Please note that all data that is generally regarded as personal
remarks: * data has been removed from this object.
remarks: * To view the original object, please query the RIPE Database at:
remarks: * http://www.ripe.net/whois
remarks: ****************************
Parent vs Child Delegations
Parent as columns, Child as rows
ARIN
IPv4
| ROOT | ASSIGNMENT | RIR | ALLOCATION | REALLOCATION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSIGNMENT | 5 | 8 | 10 | nan | nan |
| RIR | 203 | nan | 7242 | nan | nan |
| ALLOCATION | 18 | nan | 72591 | nan | nan |
| REALLOCATION | nan | nan | 391 | 42418 | 2315 |
| REASSIGNMENT | nan | nan | 679 | 2.73962e+06 | 293061 |
| RESERVED | nan | nan | 2 | nan | nan |
IPv6
| ROOT | RESERVED | RIR | ALLOCATION | REALLOCATION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSIGNMENT | 7 | 6 | 1 | nan | nan |
| RESERVED | 2 | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| RIR | 37 | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| ALLOCATION | nan | nan | 9686 | nan | nan |
| REASSIGNMENT | nan | nan | 39 | 278785 | 584 |
| REALLOCATION | nan | nan | 25 | 10255 | 108 |
LACNIC
IPv4
| ROOT | ALLOCATED | REASSIGNED | ASSIGNED | REALLOCATED | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED | 16815 | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| REASSIGNED | 2 | 108686 | 1087 | 880 | 1186 |
| REALLOCATED | nan | 305261 | 8 | 13 | 29766 |
| ASSIGNED | 2552 | nan | nan | nan | nan |
IPv6
| ROOT | ALLOCATED | REALLOCATED | ASSIGNED | REASSIGNED | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED | 11210 | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| ASSIGNED | 1560 | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| REALLOCATED | 8 | 10116 | 1367 | nan | nan |
| REASSIGNED | 7 | 2734 | 933 | 52 | 35 |
AFRINIC
IPv4
| ROOT | ALLOCATED UNSPECIFIED | POLICY-RESERVED | ALLOCATED PA | ASSIGNED PA | ASSIGNED PI | SUB-ALLOCATED PA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED UNSPECIFIED | 9 | 145 | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| ALLOCATED PA | 483 | 2879 | 3 | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| ASSIGNED PA | nan | nan | nan | 142288 | 5865 | 1 | 39 |
| SUB-ALLOCATED PA | nan | nan | nan | 360 | nan | nan | nan |
| ASSIGNED ANYCAST | nan | 10 | nan | 2 | nan | nan | nan |
| ASSIGNED PI | 496 | 980 | 146 | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| POLICY-RESERVED | nan | 5 | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan |
IPv6
| ROOT | ALLOCATED UNSPECIFIED | ALLOCATED-BY-RIR | ASSIGNED PA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED UNSPECIFIED | 1 | 2 | nan | nan |
| ALLOCATED-BY-RIR | nan | 1057 | nan | nan |
| ASSIGNED PA | nan | nan | 30715 | 55 |
| ASSIGNED PI | nan | 328 | nan | nan |
| ASSIGNED ANYCAST | nan | 3 | 1 | nan |
RIPE
IPv4
| ROOT | ALLOCATED PA | ASSIGNED PA | LIR-PARTITIONED PA | SUB-ALLOCATED PA | LEGACY | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED UNSPECIFIED | 12810 | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| ASSIGNED PA | 879 | 3.67471e+06 | 1683 | 354457 | 43318 | nan |
| ALLOCATED PA | 66978 | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| LIR-PARTITIONED PA | 11 | 11418 | 7 | 1697 | 82 | nan |
| SUB-ALLOCATED PA | 234 | 8767 | nan | 301 | 2221 | nan |
| ALLOCATED-ASSIGNED PA | 23 | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| LEGACY | 5150 | nan | nan | nan | nan | 120322 |
| ASSIGNED PI | 20258 | 1 | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| ASSIGNED ANYCAST | 50 | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan |
IPv6
| ROOT | ALLOCATED-BY-RIR | ALLOCATED-BY-LIR | AGGREGATED-BY-LIR | ASSIGNED | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED-BY-RIR | 15 | 22658 | nan | nan | nan |
| ASSIGNED | nan | 654162 | 57695 | 63231 | 32 |
| ALLOCATED-BY-LIR | nan | 11603 | 6674 | 2 | nan |
| AGGREGATED-BY-LIR | nan | 13262 | 50485 | 702 | nan |
| ASSIGNED ANYCAST | nan | 67 | nan | nan | nan |
| ASSIGNED PI | nan | 3799 | nan | nan | nan |
APNIC
IPv4
| ROOT | ALLOCATED PORTABLE | ASSIGNED PORTABLE | ALLOCATED NON-PORTABLE | ASSIGNED NON-PORTABLE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED PORTABLE | 217 | 41539 | 3 | 96 | 4 |
| ASSIGNED PORTABLE | nan | 13263 | 164 | nan | nan |
| ALLOCATED NON-PORTABLE | nan | 81252 | 54 | 13604 | 81 |
| ASSIGNED NON-PORTABLE | nan | 876538 | 180 | 215280 | 21075 |
IPv6
| ROOT | ALLOCATED PORTABLE | ASSIGNED NON-PORTABLE | ALLOCATED NON-PORTABLE | ASSIGNED PORTABLE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALLOCATED PORTABLE | 9 | 8858 | nan | nan | nan |
| ASSIGNED NON-PORTABLE | nan | 75031 | 831 | 781 | nan |
| ALLOCATED NON-PORTABLE | nan | 12257 | nan | 121 | nan |
| ASSIGNED PORTABLE | nan | 6134 | nan | nan | 6 |
Links to Policy Manuals